![]() by Joe Sivaswamy, Updated on December 9, 2022
by Joe Sivaswamy, Updated on December 9, 2022
When a semiconductor company introduces a new IC to the market, in addition to presenting technical data and other marketing material, they also offer a reference design to attract potential customers.
The reference design is provided in the form of an evaluation board. It is a proof-of-concept platform to target customers with relevant information; Information that can be used in their future designs or to upgrade their present designs. The reference design is generally targeted for specific applications. Yet the IC can be used in a broader market segment. The aim is to increase the likelihood of the IC being taken into consideration in customer designs. This is to help the manufacturer gain a competitive advantage.
The reference design helps customers to validate the IC’s performance. To ensure that the IC meets certain critical parameters of their product design.
Using Reference design board for EMC performance
It is also common practice for IC manufacturers to use the same reference design to demonstrate EMC compliance of the IC. EMC compliance is demonstrated for the targeted market by providing EMC measurement data. This EMC measurement data is important to customers when using power converters and sensors in their end products. Power converters are generally the potential emission sources, while sensors are susceptible to external emission.
EMC Simulations for reference design boards
EMC simulation can help semiconductor manufacturers in two ways. It is useful in the design of reference design boards as well as addressing end-use IC applications’ EMC compliance.
• For reference board design – pre and post-PCB design
While designing reference boards, not only should the ICs meet the EMC requirements, but the PCB too must be designed for compliance with the EMC standards.
• Pre-PCB fabrication simulation
An EMC simulation can be run on the board design before it goes to fabrication. Application engineers designing the reference design boards will have access to the PCB files (schematics, ODB++, BOM, etc..). They can import these design files into the simulation software. IC noise source model can be generated through transient simulation (in Spice simulation), or importing/generating through models features within the simulation tools.
i) PCB transfer function: EMC simulation allows characterization of the noise source (the IC) and the emission path (the PCB, cables etc.) separately. The designer can determine how the PCB transfer function influences the emission results. The designer can thus design the PCB before fabrication to reduce resonances that influence the emission results.
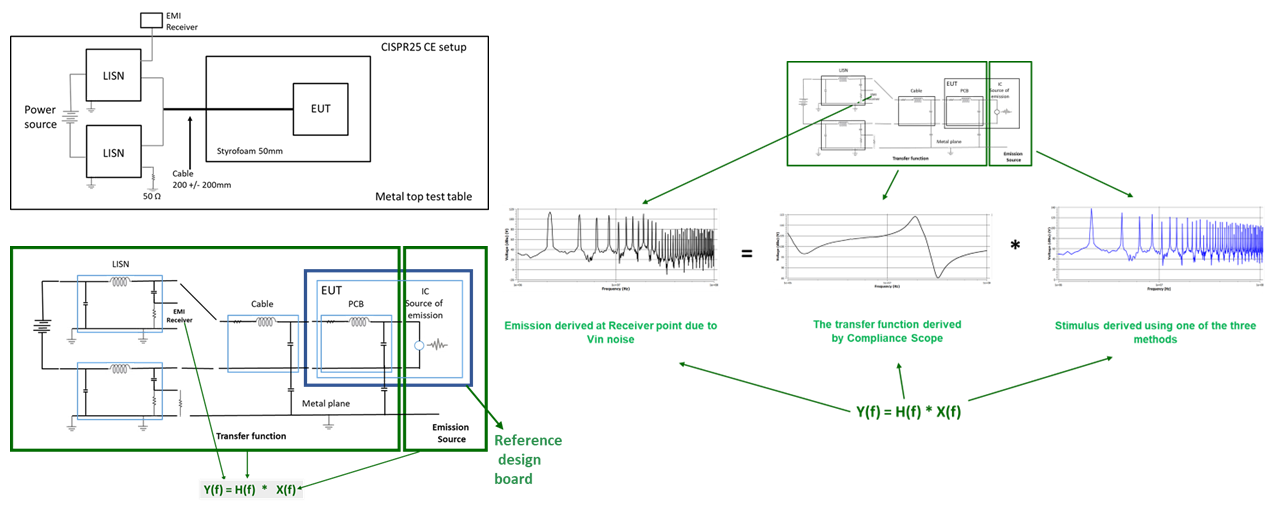
ii) Importing / generating equivalent noise source: Most IC companies offer only encrypted spice files to its end users. Whereas, they have access to unencrypted models. These models can be used for more accurate circuit simulation to derive the IC noise source for the simulation.
The simulation helps to get the PCB qualified for compliance to specific EMC standards before fabrication.
• Simulation post PCB fabrication and assembly
After the PCB gets ready and fabricated, it is also possible to make actual measured noise levels on specific IC pins. This data can be imported as a noise source into the EMC simulation to rerun the simulation. This can help to improve the noise source model for the simulation.
On measurement completion, the simulation results can be correlated to the measurement results. Both measurement and the simulation results can be provided to customers to assist in their end use applications.
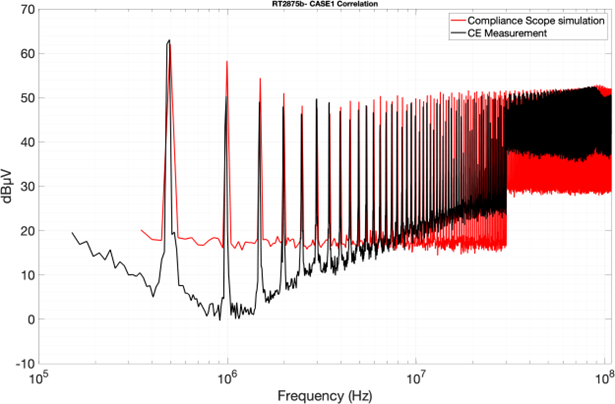
Figure 2. Correlation: Measurement Vs Simulation for Richtek RT2875B test PCB
In Part 2 of this blog series, we shall discuss how EMC simulation for reference design board is useful in application support to end users.

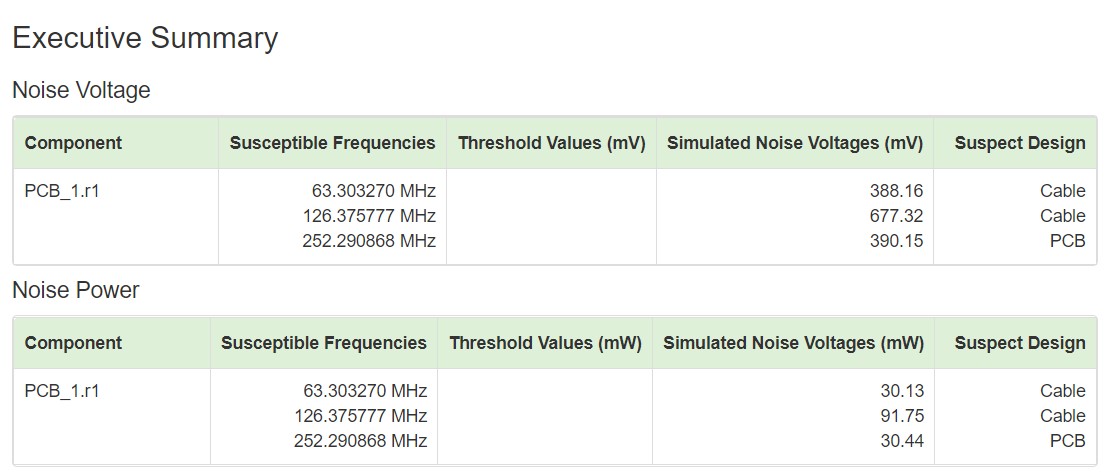 Figure 3: Diagnostics and analysis features of Simulation
Figure 3: Diagnostics and analysis features of Simulation